deleder2k
Senior Member
- Messages
- 1,130
New patent application from Øystein Fluge and Olav Mella:
ACTIVATORS OR STIMULATORS OF SOLUBLE GUANYLATE CYCLASE
FOR USE IN TREATING CHRONIC FATIGUE SYNDROME
Some key points:

Source: http://worldwide.espacenet.com/publ...T=D&ND=3&date=20150507&DB=EPODOC&locale=en_EP
Looks interesting. And it seems that this is more potent than isosorbide mononitrate (Imdur).
A major drawback is the price of Riociguat. In Norway a pack of 28 costs $4000. The drug was recently introduced. Trade name is Adempas.
ACTIVATORS OR STIMULATORS OF SOLUBLE GUANYLATE CYCLASE
FOR USE IN TREATING CHRONIC FATIGUE SYNDROME
Some key points:
ACTIVATORS OR STIMULATORS OF SOLUBLE GUANYLATE CYCLASE
FOR USE IN TREATING CHRONIC FATIGUE SYNDROME
The present invention relates in a first aspect to a method for the treatment of chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) comprising administering to a patient in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of a stimulator of the soluble guanylate cyclase and/or a therapeutically effective amount of an activator of the soluble guanylate cyclase. In a further aspect, the present invention relates to a combination of the stimulator and/or activator of the soluble guanylate cyclase with a B-cell depleting agent in the treatment of chronic fatigue syndrome. In addition, a combination of stimulator and/or activator of the soluble guanylate cyclase and B-Cell depleting agent are described. Said combination may be provided in form of a kit comprising suitably effective dosages of said compounds.
The guanylate cyclase, also known as guanylyl cyclase or guanyl cyclase, EC 4.6.1 .2, (GC) is a lyase enzyme catalysing deformation of guanosine 3', 5'- monophosphate (cGMP) from guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and is found in tissues throughout the animal kingdom. Soluble GC (sGC) is the receptor for nitric oxide (NO) in vascular smooth muscle. In the cardiovascular system, NO is en- dogenously generated by endothelial NO synthase. Involvement of NO and sGC is described in stress and it appears that the NO-sGC-cGMP pathway is relevant for the control of a number of physiologic processes, including neuronal transmission, host defense, cell growth and proliferation as well as vascular and platelet homeostasis.
Stimulation of sGC mediates physiologic responses including smooth muscle relaxation, inhibition of inflammation and thrombosis. Hence, sGC represents a target for drugs in the treatment of various diseases. In general, two classes of compounds have been developed, that can directly activate sGC in pathophysiologic conditions when NO formation and bioavailability are impaired or when NO tolerance has developed. That is, heme-dependent stimulators and heme- independent activators of sGC have been described. For example, potent stimulators are described in a series of patent applications, e.g. WO 03/097063, WO 02/42302, WO 02/42299, WO 03/095451 and WO 03/004503.
However, as indicated above, using B-cell depletion by the monoclonal an- ti-CD20 antibody Rituximab in CFs, there is a significant delay from start of the treatment and the beginning of the symptoms relief. Also, the clinical studies performed with Rituximab, approximately 2/3 of CFS patients have a clinical response. This is not only true for treatment with Rituximab, but can also be seen with treatment of methotrexate, a small molecule known as an active agent for B- cell depletion useful in the treatment of various kinds of diseases.
Thus, there is an ongoing need to provide additional compounds useful in the treatment of chronic fatigue syndrome. In particular, there is an ongoing need for providing compounds which act fast in the patients without the lag period described for the B-cell depleting agent. In addition, there is a continuous demand for compounds which may also be effective in patients not susceptible to B-cell depleting agent treatment.
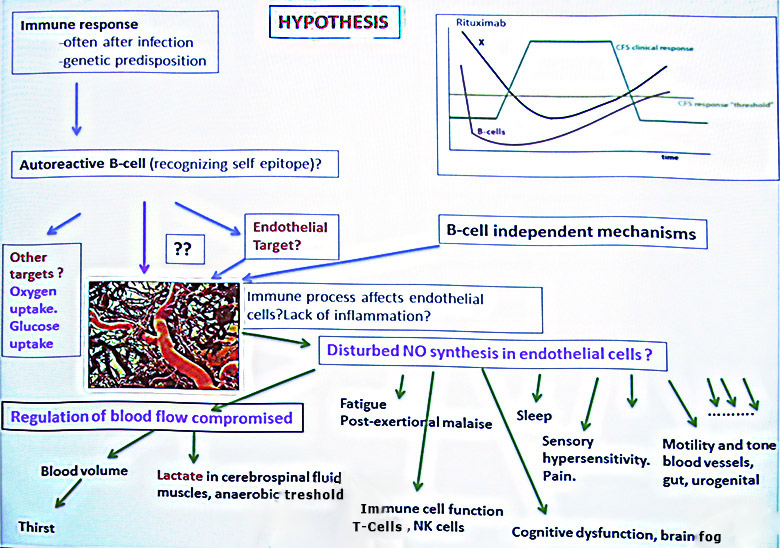
CFS patients have a marked endothelial dysfunction assessed by Flow- Mediated Dilation (FMD), a test that (under standardized conditions) largely reflect Nitric Oxide (NO) synthesis in endothelial cells after shear stress. A markedly reduced FMD, transient clinical responses after long-acting nitrates (like isosorbide mononitrate) and the clinical picture of CFS, are the basis for a hypothesis according to the present invention in which a main mechanism for CFS symptom maintenance is a relative lack of endothelial-cell derived Nitric Oxide (NO) availability. This results in reduced NO diffusion from endothelial cells to surrounding cells such as smooth muscle cells in blood vessel walls, and with a resulting inadequate regulation of blood flow to meet the metabolic demands of tissues. Also a relative lack of endothelial-cell derived NO may result in cognitive disturbances, sleep problems, a low anaerobic threshold, and lactate accumulation in tissues after modest exertion, a low NK cell function, all reported to be associated with CFS.
Description of the present invention
In a first aspect, the present invention relates to a method for the treatment of chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) comprising administering to a patient in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of a stimulator of the soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) and/or a therapeutically effective amount of an activator of the soluble guanylate cyclase.
That is, the present inventors recognized that administration of an activator of sGC and/or a stimulator of sGC, e.g. Cinaciguat or Riociguat, relieve the symptoms of CFS and, thus, may be useful in the treatment of CFS, accordingly.
In particular, the present inventors recognized that an immediate relief, e.g. within a week, from start of administration of said activator or stimulator of sGC, e.g. by carefully increasing the dose, can be observed. In contrast to medication such as Rituximab for a treatment of CFS, which is characterized by a remarkable lag time before clinical responses, as described, e.g. WO 2009/083602. Hence, the administration of the stimulator and activator of sGC surprisingly allow a treatment of CFS patients for early relief of symptoms without a long delay as described for e.g. a B-Cell depleting agent, like Rituximab. It is has been recognized by the inventors that the sGC is involved in therapy of CFS patients.

Source: http://worldwide.espacenet.com/publ...T=D&ND=3&date=20150507&DB=EPODOC&locale=en_EP
Looks interesting. And it seems that this is more potent than isosorbide mononitrate (Imdur).
A major drawback is the price of Riociguat. In Norway a pack of 28 costs $4000. The drug was recently introduced. Trade name is Adempas.
Last edited: