nanonug
Senior Member
- Messages
- 1,709
- Location
- Virginia, USA
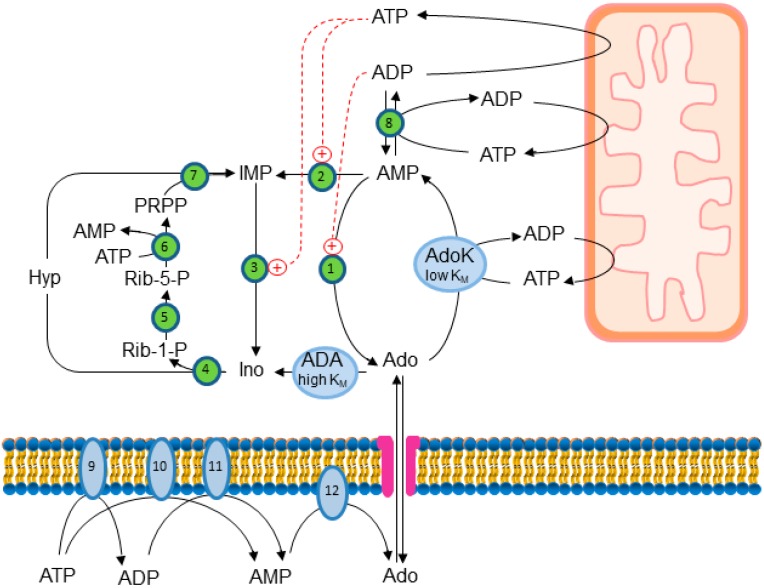
COMMENT: This is a beautifully written article about adenosine. It shows all the important directly connected metabolic pathways, including those with AMP, ADP and ATP, both inside and outside of the cell. Great reading for those interested in a better understanding of bioenergetics and purinergic signaling.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5877645/
Abstract
Several physiological functions of adenosine (Ado) appear to be mediated by four G protein-coupled Ado receptors. Ado is produced extracellularly from the catabolism of the excreted ATP, or intracellularly from AMP, and then released through its transporter. High level of intracellular Ado occurs only at low energy charge, as an intermediate of ATP breakdown, leading to hypoxanthine production. AMP, the direct precursor of Ado, is now considered as an important stress signal inside cell triggering metabolic regulation through activation of a specific AMP-dependent protein kinase. Intracellular Ado produced from AMP by allosterically regulated nucleotidases can be regarded as a stress signal as well. To study the receptor-independent effects of Ado, several experimental approaches have been proposed, such as inhibition or silencing of key enzymes of Ado metabolism, knockdown of Ado receptors in animals, the use of antagonists, or cell treatment with deoxyadenosine, which is substrate of the enzymes acting on Ado, but is unable to interact with Ado receptors. In this way, it was demonstrated that, among other functions, intracellular Ado modulates angiogenesis by regulating promoter methylation, induces hypothermia, promotes apoptosis in sympathetic neurons, and, in the case of oxygen and glucose deprivation, exerts a cytoprotective effect by replenishing the ATP pool.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5877645/
Abstract
Several physiological functions of adenosine (Ado) appear to be mediated by four G protein-coupled Ado receptors. Ado is produced extracellularly from the catabolism of the excreted ATP, or intracellularly from AMP, and then released through its transporter. High level of intracellular Ado occurs only at low energy charge, as an intermediate of ATP breakdown, leading to hypoxanthine production. AMP, the direct precursor of Ado, is now considered as an important stress signal inside cell triggering metabolic regulation through activation of a specific AMP-dependent protein kinase. Intracellular Ado produced from AMP by allosterically regulated nucleotidases can be regarded as a stress signal as well. To study the receptor-independent effects of Ado, several experimental approaches have been proposed, such as inhibition or silencing of key enzymes of Ado metabolism, knockdown of Ado receptors in animals, the use of antagonists, or cell treatment with deoxyadenosine, which is substrate of the enzymes acting on Ado, but is unable to interact with Ado receptors. In this way, it was demonstrated that, among other functions, intracellular Ado modulates angiogenesis by regulating promoter methylation, induces hypothermia, promotes apoptosis in sympathetic neurons, and, in the case of oxygen and glucose deprivation, exerts a cytoprotective effect by replenishing the ATP pool.

Last edited:
